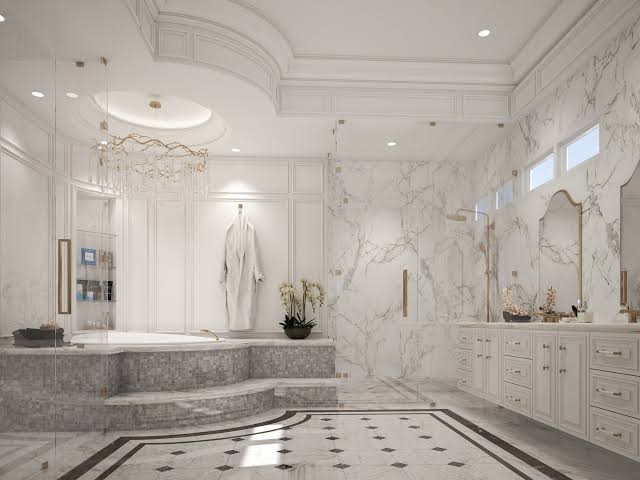
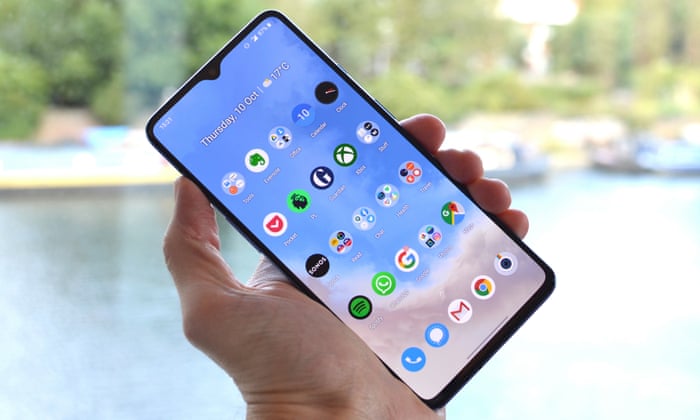
Description
Amenities


Safety Requirements

Cancellations
Cancellation Policy :
Cancel the booking more than 72 hours before the rental period starts to avoid any charges. If the booking is canceled between 72 hours and 24 hours before the rental period starts, a cancellation fee will be deducted.
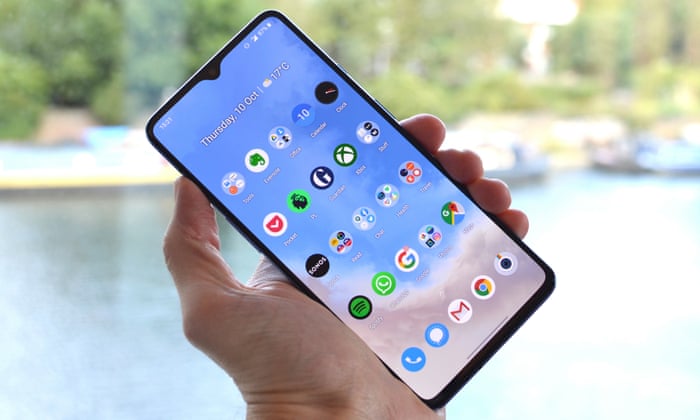
Description
Amenities


Safety Requirements

Cancellations
Cancellation Policy :
Cancel the booking more than 72 hours before the rental period starts to avoid any charges. If the booking is canceled between 72 hours and 24 hours before the rental period starts, a cancellation fee will be deducted.
Similar Listings
Listing General Location
Madurai, Tamil Nadu, India
No reviews yet
Be the first to review! Reserve now.
The listing owner, yash
Has been a proud contributor since September 2024.